
- Harsh Maur
- December 17, 2025
- 9 Mins read
- WebScraping
How to do Udemy Web Scraping?
Udemy web scraping involves automating the process of extracting course data like titles, prices, ratings, and enrollment numbers from the Udemy platform. This data can help businesses analyze market trends, monitor competitors, and refine strategies. However, scraping must follow legal and ethical guidelines, including respecting Udemy's Terms of Service and avoiding restricted areas outlined in their robots.txt file.
Key steps include:
- Identifying data fields: Extract course details, pricing, instructor info, and performance metrics.
- Choosing tools: Use Python libraries like Beautiful Soup, Requests, or advanced tools like Selenium for dynamic pages.
- Ensuring compliance: Use rate limiting, avoid personal data, and consider APIs for approved access.
- Organizing data: Save in CSV or JSON formats for easy analysis.
For larger projects, managed services like Web Scraping HQ can simplify the process by handling legalities, infrastructure, and data delivery.
Takeaway: Udemy web scraping can provide actionable insights for businesses, but it requires careful planning, the right tools, and strict adherence to legal standards.
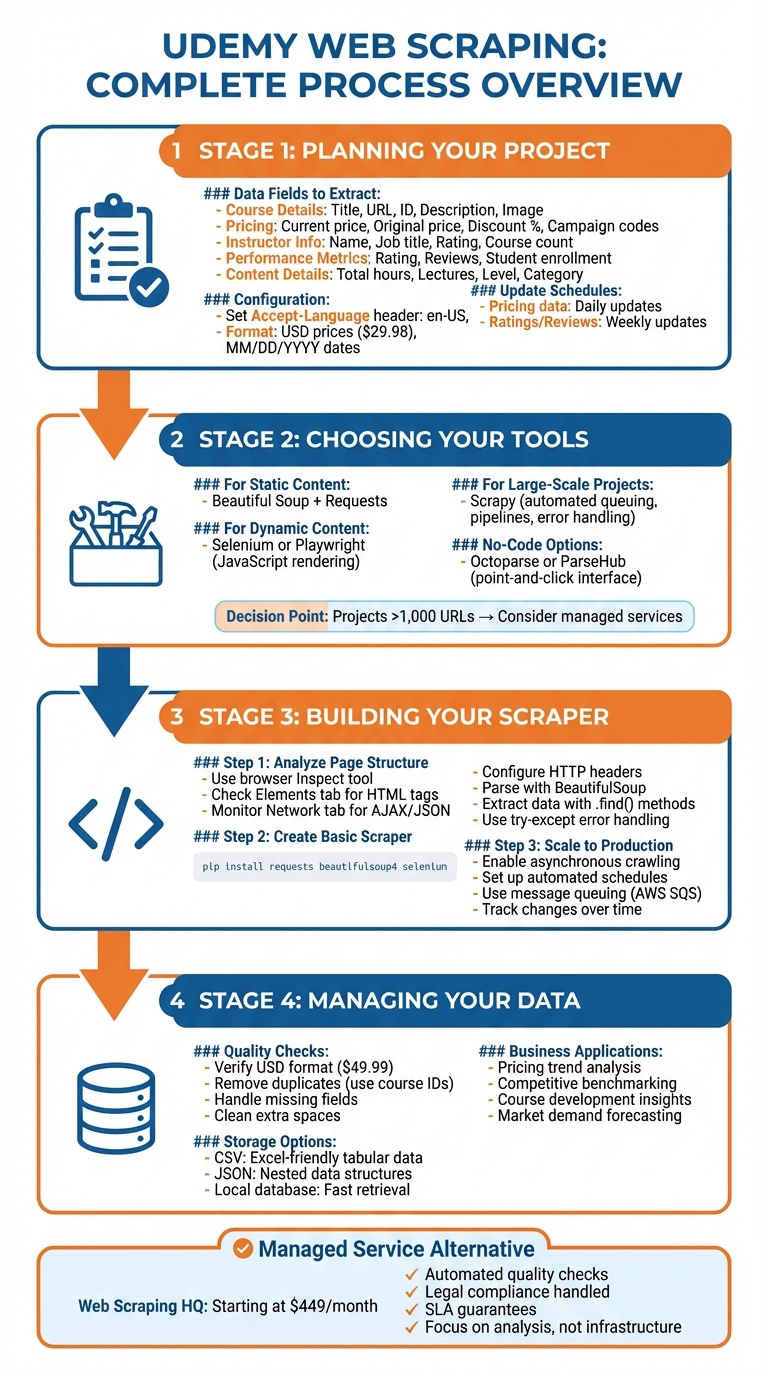
Udemy Web Scraping Process: 4-Step Guide from Planning to Implementation
Planning Your Udemy Web Scraping Project
Selecting Data Fields to Extract
To kick off your Udemy web scraping project, start by identifying the data fields that align with your goals. Commonly extracted fields include course details like title, URL, course ID, description, and image URL. Pricing information is also key - this includes the current price, original price, discount percentage, and any campaign codes. On the instructor side, gather details such as name, job title, rating, and the number of courses offered. Performance metrics like course rating, number of reviews, and total student enrollment are essential for evaluating course popularity.
If you're diving into content analysis, capture specifics like total hours, number of lectures, instructional level (beginner, intermediate, expert), and the primary category. For a deeper look, you might also want to extract details about the course structure, such as curriculum items, quiz counts, and learning outcomes.
Once you've gathered this data, organize it in either CSV or JSON format. CSV is great for simple tabular data, while JSON is better suited for handling nested details, like instructor profiles or discount structures.
Configuring U.S. Regional Settings
When scraping Udemy, it’s important to ensure your data reflects U.S. standards. This means formatting prices, dates, and numbers correctly. To achieve this, include an Accept-Language HTTP header in your requests, setting it to en-US,en;q=0.8. This signals to Udemy’s servers that you need content tailored for U.S. audiences.
For example, prices will appear in the U.S. format with a dollar sign (e.g., $29.98), while numbers will use commas as thousands separators and periods for decimals (e.g., "3,820 reviews"). Dates will follow the MM/DD/YYYY format, which is standard in the United States. If your scraper interacts with billing forms, be prepared to handle ZIP codes, as these are often required for U.S. users.
Setting Update Schedules
Once your data fields are set, decide how often to update your scraper. Pricing data tends to fluctuate frequently, especially during Udemy’s promotional campaigns, so daily updates are ideal for capturing changes. On the other hand, metrics like course ratings and review counts evolve more slowly, making weekly updates sufficient for most projects.
Keep an eye on the "last updated" field for each course to determine when a re-scrape is necessary. Fast-changing topics, such as technology or digital marketing, may require more frequent updates compared to more stable subjects. Tailor your scraping schedule based on how quickly the data changes in your chosen categories.
Tools and Methods for Udemy Web Scraping
Common Web Scraping Tools
When it comes to scraping Udemy, Python libraries like Beautiful Soup and Requests are excellent for extracting static HTML content. However, Udemy's dynamic pages often require more advanced solutions. Tools like Playwright and Selenium - headless browsers capable of rendering JavaScript - are better equipped to handle dynamic content.
If you're working on larger-scale projects, consider Scrapy, a powerful web scraping framework. It can handle multiple course pages efficiently by automating tasks like request queuing, data pipelines, and error handling. This can save a lot of time during development. For those without programming skills, visual tools like Octoparse and ParseHub provide point-and-click interfaces. However, keep in mind that these tools might struggle with Udemy's anti-bot measures and complex page structures.
Each of these tools has its strengths, making them suitable for projects of varying sizes and complexities. As your project scales, you may find it worthwhile to explore managed services for even greater efficiency.
When to Consider a Managed Service
If your scraping needs are small - say, a handful of pages - a custom scraper will likely do the job. But as your project grows to include more than 1,000 URLs or requires frequent updates, the technical challenges can quickly pile up. This is where managed services come into play.
Managed services are particularly useful if your team’s focus is on analyzing data rather than maintaining scraping infrastructure. They handle the heavy lifting, from managing automation challenges to ensuring compliance with privacy laws and terms of service. This legal aspect can be especially tricky to navigate without dedicated expertise, making outsourcing a smart choice for larger projects.
Advantages of Managed Solutions
Managed solutions, like Web Scraping HQ, simplify the entire process by delivering clean, structured data in formats like JSON or CSV. They enforce schemas, validate fields, and remove duplicates automatically, saving you the hassle of debugging and cleaning up data.
Another perk is the reliability offered through Service Level Agreements (SLAs). These agreements ensure guaranteed uptime and consistent data delivery schedules, helping you stay on track with your analysis. By outsourcing the scraping process, you can focus fully on deriving insights from the data rather than worrying about the technical details of extraction.
How to Build a Udemy Web Scraper
Analyzing Udemy Page Structure
To scrape Udemy effectively, the first step is to analyze the structure of its pages. Open a course page, right-click anywhere, and select "Inspect" to launch your browser's developer tools. In the Elements tab, you can navigate through the HTML structure, expanding sections and hovering over elements to pinpoint the data you're after. Look for tags like <div>, <a>, <img>, and <span> that typically hold key details such as course titles, instructor names, ratings, prices, and enrollment numbers.
For an even more efficient approach, switch to the Network tab to monitor AJAX requests. These often fetch JSON data, which can be easier to scrape than parsing complex HTML layouts.
Creating a Basic Scraper
Once you understand how Udemy's pages are structured, you can start building your scraper. Begin by installing the necessary Python libraries using:
pip install requests beautifulsoup4 selenium
To reduce the risk of being blocked, configure your scraper to mimic a real browser. Set up HTTP headers by including fields like Accept, Accept-Encoding, and Accept-Language. Then, use a command like this to fetch page content:
requests.Session().get(url, headers=req_headers, timeout=(5, 60))
Parse the fetched content with BeautifulSoup:
BeautifulSoup(r.content, 'html.parser')
To extract specific data, use methods like soup.find() or soup.find_all() with attributes such as class or id. For example, to locate instructor stats, you might use:
soup.find('div', attrs={'class': 'instructor--instructor__image-and-stats--1MRZH'})
Extract text using the .text property or retrieve attributes like ['alt'] from image tags. If you need to match specific patterns, regular expressions can help. For example, use r"^/user/?" to identify instructor profile URLs or r"^https://linkedin.com/?" for social media links. Always wrap your requests in try-except blocks to handle errors gracefully.
Expanding to Production Scale
If you're planning to scrape thousands of pages, you'll need a more robust setup. Tools like Scrapy allow for asynchronous crawling, enabling you to scrape multiple pages simultaneously. Adjust concurrency settings to speed up the process.
For ongoing data collection, set up automated schedules to run your scraper at regular intervals - whether daily or weekly - to ensure your data stays up to date. You can also use message queuing systems like AWS SQS to manage tasks across distributed workers, making your scraper more scalable and reliable.
When storing the data, organize it in a structured format. Remove duplicates by checking unique identifiers like course IDs, and track changes over time by comparing new data with previous versions. This approach ensures your data remains accurate and actionable, giving you a solid foundation for making informed decisions. Once your scraper is running at scale, focus on improving how you manage and utilize the collected data for maximum impact.
sbb-itb-65bdb53
Managing and Using Your Scraped Data
Data Quality Checks
Once you've completed your Udemy web scraping, the first order of business is ensuring the data you’ve gathered is accurate and complete. Double-check that USD prices follow the proper format (e.g., $49.99), strip out unnecessary terms like "Sale price", and clean up any extra spaces. It’s also crucial to implement error handling for issues like HTTP timeouts to make sure you’re not missing any data. Look out for missing fields, duplicate entries, or formatting inconsistencies - these can all skew your analysis.
Taking the time to clean and standardize your data ensures it’s ready for meaningful analysis. Once your data is polished, the next step is organizing it for storage and easy access.
Organizing Data for Storage
After confirming your data is accurate and properly formatted, it’s time to organize it in a structured way. Tools like Pandas DataFrames in Python are particularly useful for handling tabular data, such as course names, instructor details, and categories.
"The data frame (df) now holds the extracted data in a structured tabular format, making it easier to analyze and manipulate using pandas functionalities."
To keep things efficient, save your data in formats like CSV or JSON. CSV files are great for working in Excel, while JSON is better suited for feeding data into apps or APIs. For even more efficiency, consider storing the data in a local database or cache. This not only speeds up data retrieval but also reduces the need for repeated scraping. Use unique identifiers, like course IDs, to avoid duplicates, and maintain version histories to track changes over time.
Applying Data to Business Decisions
With clean, well-structured data in hand, you can start using it to inform your business strategies. For example, comparing current prices to original ones can reveal pricing trends, while tracking student enrollment numbers highlights popular topics and market demand.
Your scraped data can also provide valuable insights for competitive analysis. By examining course offerings, instructor ratings, and review sentiment, you can spot emerging trends or shifts in your niche. If you’re creating courses yourself, studying successful competitors can offer inspiration for content that resonates with students. Tracking enrollment figures and ratings over time can help predict which topics are likely to succeed. This kind of data-driven approach enables smarter decisions about course development, pricing strategies, and marketing efforts - all based on actual market behavior, not guesswork.
Conclusion
Using Udemy web scraping opens the door to valuable market insights that can reshape your online education strategies. By pulling data like course prices, enrollment figures, instructor ratings, and student feedback, you gain a clear picture of what works in your niche and where fresh opportunities might exist. This takes you from relying on guesswork to making decisions based on real market trends and behaviors.
On the technical side, web scraping requires a solid understanding of page structures, handling dynamic content, and keeping your tools updated as websites evolve. Popular tools like Beautiful Soup and Selenium can help, but building a reliable scraper also involves managing proxies, troubleshooting errors, and ensuring you operate within legal and ethical boundaries. These challenges often make outsourcing a practical solution.
For businesses without the technical know-how, managed services can be a game-changer. Providers like Web Scraping HQ offer both DIY and fully managed options, handling the complexities for you. Starting at $449/month for the Standard plan, these services include automated quality checks, legal compliance, and expert support. This lets you focus on using the data, rather than worrying about how to get it.
Whether you’re tracking competitor pricing, keeping an eye on trending topics, or evaluating instructor performance, Udemy web scraping equips you with the data you need for smarter, faster decisions. The right approach - whether building your own scraper or opting for a managed service - can help you sidestep technical challenges and fully harness the potential of this powerful tool.
FAQs
Get all your questions answered about our Data as a Service solutions. From understanding our capabilities to project execution, find the information you need to make an informed decision.
Yes, it is legal to scrape publicly available data.
Webscraping HQ’s scraping tool is Best for Web scraping. You can Try their Web scraping API for Free.
It is possible to extract Courses from Udemy. Here are the steps to extract Courses from Udemy. *Visit to Webscraping HQ website *Login to web scraping API *Paste the url into API and wait for 2-3 minutes *You will get the scraped data.