
- Harsh Maur
- January 1, 2026
- 11 Mins read
- WebScraping
How to scrape 99acres Data?
Scraping data from 99acres, a major Indian real estate platform, involves extracting key property details like prices, locations, and specifications using Python tools. Here’s how you can do it effectively:
- Tools Needed: Use Python libraries such as Playwright or Selenium for handling JavaScript-rendered pages, BeautifulSoup for parsing static HTML, and Pandas for organizing data.
- Key Challenges: 99acres uses JavaScript to load dynamic content and implements anti-scraping measures like CAPTCHAs and IP blocking. Advanced sites may also require specialized techniques to bypass Cloudflare protections during the extraction process.
- Solutions: Deploy browser automation tools for dynamic content, use residential proxies to manage IPs, and include delays between requests to mimic human behavior.
- Data Cleaning: Convert prices (e.g., "₹2.5 Cr") into numerical formats, standardize dates, and deduplicate entries.
- Legal Considerations: Always review 99acres' terms of service and ensure ethical scraping practices, like respecting rate limits and avoiding personal data collection.
This process helps collect structured data for market research, price tracking, and business analysis while ensuring compliance and efficiency.
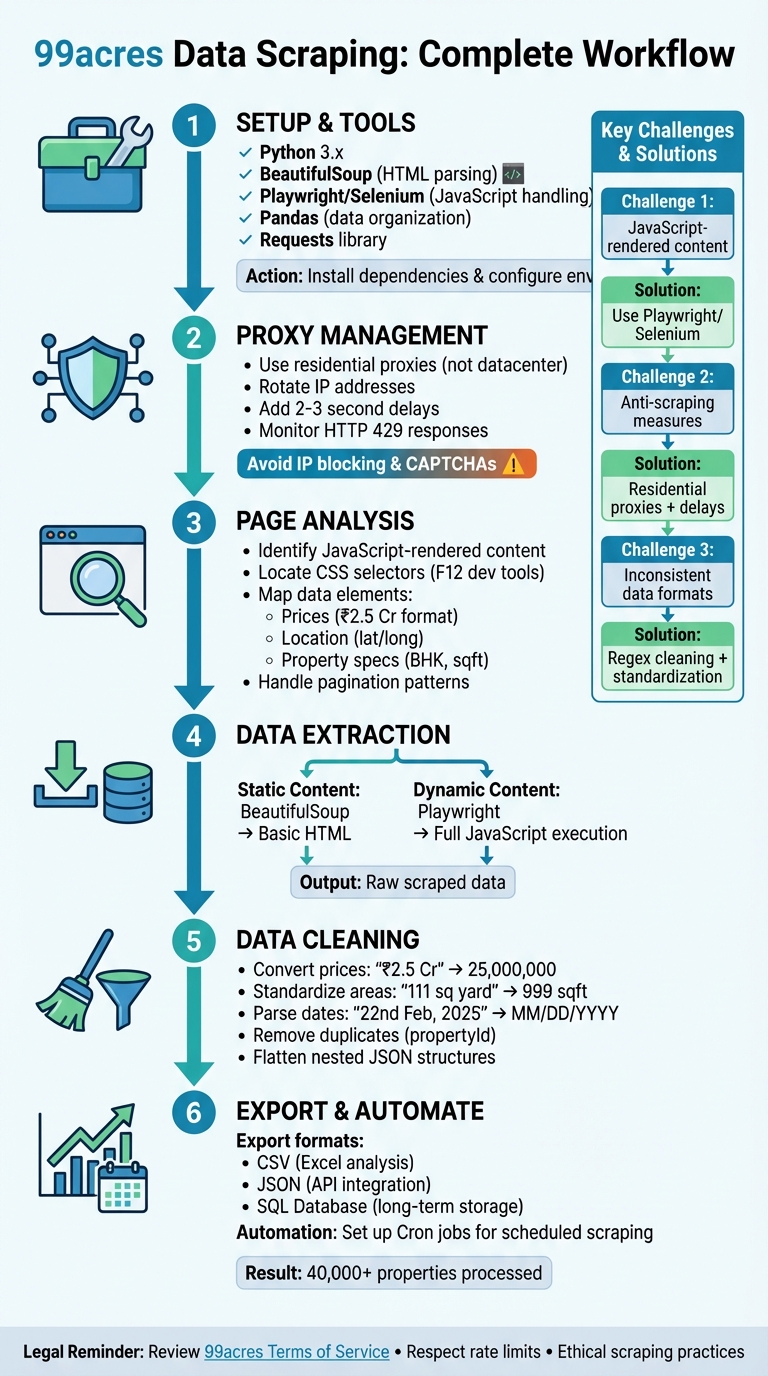
Complete 99acres Web Scraping Workflow: From Setup to Analysis
Setting Up Your Tools and Environment
Required Tools and Software
To get started with your scraping project, you'll need Python 3.x as the foundation. For parsing HTML and extracting data, BeautifulSoup (BS4) is the go-to library. When dealing with dynamic content or JavaScript-rendered elements, you’ll need tools like Playwright or Selenium, as static parsers alone won’t cut it. The Requests library helps you send HTTP requests to the 99acres servers, while Pandas organizes the extracted data into user-friendly formats like CSV or Excel for further analysis.
Here’s how it all works together: Playwright or Selenium handles dynamic page loading, BeautifulSoup takes care of parsing the HTML, and Pandas formats the results into structured datasets. Before diving in, you’ll need to install these tools and set up your environment.
Installing Dependencies
Start by creating a virtual environment to keep your project isolated and free from dependency conflicts. Use the command:
python -m venv scraper_env
Activate the virtual environment, then install the required libraries. For Playwright, run:
pip install playwright
playwright install
This ensures browser binaries are ready to go. Next, install other essential libraries:
pip install beautifulsoup4 pandas requests
While developing, set headless=False in Playwright to see the browser in action. This makes debugging much easier when interacting with 99acres' elements. To keep your setup secure and modular, store sensitive information and base URLs in a .env file.
With everything installed, you’ll also need to configure proxies to manage your IPs effectively for scraping.
Proxy and IP Management
If you’re planning large-scale scraping on 99acres, residential proxies are a must. These proxies use real internet connections, making them far less likely to be flagged compared to datacenter proxies. Rotating through a pool of IP addresses is another important step - it prevents any single IP from making too many requests, which could trigger security measures on the site.
To mimic human behavior and avoid detection, add delays of 2-3 seconds between requests. Residential proxies are especially useful because they provide legitimacy, and using proxies based in India ensures you’re accessing the local version of 99acres without encountering geo-restrictions.
Avoid using free proxy lists - they’re often unreliable and flagged by major websites. Instead, invest in trusted proxy services. Also, keep an eye on common web scraping errors and HTTP response codes during scraping. If you encounter a "429 Too Many Requests" response, slow down your requests to avoid getting permanently banned. Proper proxy management is key to a smooth and efficient scraping process.
Understanding 99acres Page Structure
Before diving into coding, it's crucial to grasp how 99acres structures its data. The site relies heavily on JavaScript-rendered content, which means many property details - like prices, locations, and amenities - load dynamically after the initial HTML. If you fetch the raw HTML using a basic request, you'll notice these elements are often missing. However, when you view the page in your browser, everything appears intact. This happens because the site populates key details only after the page fully loads. Understanding this behavior is essential for creating effective scraping scripts.
Identifying Key Data Elements
When analyzing 99acres property listings, focus on the structured data fields:
- Price Information: Prices appear in various formats, including a minimum price, maximum price, price per square foot, and a display price like "12 L" (12 lakh rupees).
- Location Details: These include latitude and longitude coordinates, text-based addresses, neighborhood names, and ZIP codes.
- Property Specifications: Look for details such as the number of bedrooms and bathrooms, built-up area, property orientation (e.g., North-East facing), property age, and the total number of floors. Additional tags like "Corner Property", "Ready to Move", or "Local Authority Approved" also provide valuable insights.
To locate these elements in the HTML, use your browser's developer tools (press F12) to inspect the page. Identify the relevant CSS selectors or XPath expressions for each data point you need to extract.
Handling JavaScript-Rendered Content
Since 99acres relies on JavaScript to load essential details, static parsers like BeautifulSoup often fall short. Instead, you'll need tools such as Selenium or Playwright, which can automate a real browser and allow the JavaScript to execute fully. This approach ensures the DOM is completely populated before you start extracting data.
For example, if price details take a few seconds to load, you can use Playwright's wait_for_selector() method to pause until the relevant elements appear. Similarly, browser automation tools help navigate issues like authorization challenges that often arise with basic HTTP requests by mimicking real user behavior.
Pagination Patterns on 99acres
Property listings on 99acres are spread across multiple pages, and the site uses two main pagination methods:
-
Traditional Pagination: Here, you'll find "Next" buttons or query parameters in the URL, such as
?page=1or?start=0. These can be iterated programmatically to scrape data across pages. - Infinite Scrolling: In this setup, new listings load dynamically as you scroll. To handle this, open your browser's Network tab and filter by XHR or Fetch requests to pinpoint the API calls triggered during scrolling. Directly targeting these APIs is often faster and more efficient than parsing the HTML. If you're using Playwright, you can automate scrolling by executing JavaScript commands that simulate user actions, triggering the loading of additional content.
Building and Running a Web Scraper
Now that you've got a handle on how 99acres structures its content, it's time to create a scraper that gets the job done. The method you choose will depend on whether you're dealing with static HTML or content rendered dynamically with JavaScript. Since much of the property data on 99acres loads dynamically, you'll probably need to combine both approaches.
Extracting Static Content with Beautiful Soup
Start by pulling data that loads directly with the page's initial HTML using Beautiful Soup. This library is a great tool for parsing static HTML. While 99acres relies heavily on JavaScript, some basic information - like property URLs or page layout - can still be grabbed using this lightweight method. First, install the necessary libraries in a virtual environment:
pip install beautifulsoup4 requests pandas
Once that's done, use the requests library to fetch the HTML and parse it with Beautiful Soup.
But here's the catch: important details like prices, locations, and amenities are often missing from the raw HTML. These elements are only loaded after JavaScript runs. If you try using static scraping methods, like converting curl commands to Python, you'll quickly hit a wall. This limitation is where static scraping falls short for sites like 99acres.
Handling Dynamic Content with Playwright
To tackle dynamic content, Playwright is your best bet. It simulates a full browser environment, allowing JavaScript to execute and load all the data you need. Start by installing Playwright:
pip install playwright
Then, run the following command to set up the required browser binaries:
playwright install
Playwright works seamlessly with Python's asyncio for asynchronous tasks. Launch a headless Chromium browser, navigate to your target URL using page.goto(), and wait for key elements - like property cards - to load using page.wait_for_selector(). Once the content is ready, use methods like query_selector_all to grab multiple elements or inner_text() to extract specific details like prices or property sizes.
To scrape multiple pages, identify the "Next" button and automate navigation. You can also use page.route() to block unnecessary resources like ads or images, speeding up the process. Since 99acres has anti-scraping measures in place, consider using residential proxies to avoid IP bans. Finally, always call browser.close() to free up resources when you're done. This dynamic scraping approach fills in the gaps left by static methods, giving you a more complete dataset.
Organizing Extracted Data
Once you've gathered the data, structuring it properly is key. Whether you’re using static or dynamic scraping methods, organizing the results will make analysis much easier. For simple, flat data, exporting to CSV is a great option - it works well with tools like Pandas. On the other hand, if you're dealing with complex fields like nested amenities or location coordinates, JSON is a better choice since it preserves hierarchical data structures.
When saving your data, include helpful metadata like scraped_at timestamps and source_url to track when and where the information came from. Stick to clear and consistent naming conventions, such as price_per_sqft or possession_status, to make merging datasets from different sessions easier. If you're working on a long-term project, consider using a SQL database with an ORM like Django to handle data storage and management efficiently. This way, you'll have a solid foundation for scaling your scraping efforts.
sbb-itb-65bdb53
Scaling and Automating the Scraping Process
Once your scraper is built and your data is neatly organized, the next step is to scale and automate the process. To handle thousands of listings without running into bans, residential proxies are a must. They’re much more reliable than datacenter proxies when it comes to bypassing anti-scraping defenses. For instance, one open-source project successfully collected over 40,000 property details from various Indian cities using Python-based tools, proving that large-scale data gathering is entirely achievable with the right setup.
Managing Large-Scale Data Collection
To keep things manageable, use a maxItems parameter to control how much data you scrape during each session. This not only avoids overloading servers but also helps keep your scraping costs predictable. Python’s asyncio is a great tool for handling multiple requests at once, and you can add randomized delays to mimic human browsing behavior and reduce the risk of detection. If you encounter authorization errors, make sure to rotate your proxies immediately.
Automating Tasks with Scheduling
Automating your scraping tasks can save you a lot of time. Tools like Cron jobs allow you to schedule scrapes at regular intervals. For Django users, integrating django-crontab is straightforward - just run python manage.py crontab add to set up recurring tasks. Before scheduling, double-check your target URLs and configurations in the .env file to ensure the scraper works seamlessly across different locations. If you’re operating in the cloud, look for cost-efficient solutions with built-in schedulers to trigger your scrapers automatically.
Automation works best when paired with solid monitoring and error-handling systems.
Monitoring and Error Handling
To keep your scraping operations running smoothly over the long term, constant monitoring is essential. Build exception handling into your scraper to deal with issues like end-of-pagination errors. Track metadata such as "updated" and "expiry" dates in property listings to avoid collecting outdated information. Cloud-based monitoring tools can provide real-time logs and status updates, helping you quickly identify and resolve problems. Adding timestamps to your exported files (e.g., 99acres_data_08262023.csv) is another good practice. It not only helps you monitor data freshness but also ensures continuity with your earlier data organization efforts.
Data Cleaning and Structuring for Analysis
Raw data from 99acres often includes strings like "₹2.5 Cr", "12 L", "22nd Feb, 2025", or "2 BHK", which need to be converted into standardized formats for effective analysis.
Cleaning Raw Data
Start by addressing price conversions. In Indian real estate, prices are commonly expressed in Lakhs (L) and Crores (Cr), where 1 Lakh equals 100,000 and 1 Crore equals 10,000,000. Using Python's re module, you can strip symbols (₹, commas) and convert entries like "₹2.5 Cr" into 25,000,000. Similarly, for area measurements, standardize everything to a single unit, such as square feet. For example, "111 sq yard" can be converted to 999 square feet by multiplying by 9, which simplifies price-per-square-foot calculations. Use regex to extract numerical values from mixed strings like "2 Baths", converting them to integers for consistent filtering and analysis.
To avoid duplicate entries, identify listings with unique fields like propertyId or url. Additionally, review the "expiry" and "updated" dates in the dataset to filter out outdated listings.
Standardizing Data Formats
Once the raw data is cleaned, focus on standardizing fields like dates, locations, and statuses. Dates in 99acres data might appear as "22nd Feb, 2025" or as ISO timestamps like "2024-09-13T06:12:51.000Z." Convert all dates into a uniform format, such as MM/DD/YYYY for U.S.-focused projects or YYYY-MM-DD for database compatibility. For location data, use latitude and longitude coordinates from the scraped JSON instead of text-based locality names, which can vary due to spelling inconsistencies. Similarly, standardize possession statuses into simplified labels like "Ready" or "Under Construction" to streamline analysis of market readiness.
Modern scrapers often produce nested JSON structures that include details like amenities, verification statuses, and geographic coordinates. Flatten these structures before exporting the data into formats like CSV or Excel, as most business tools are not equipped to handle deeply nested data. Python's Pandas library is particularly useful here, as it can quickly transform complex dictionaries into clean, tabular DataFrames. These steps ensure the processed 99acres data integrates smoothly with business intelligence tools.
Exporting for Business Use
After cleaning and standardizing the data, export it in formats tailored to your analysis needs. Use Pandas' to_csv() function to save the data locally, and include a timestamp in the filename (e.g., 99acres_data_08262023.csv) to manage version control and track updates. For database integration, Django's ORM simplifies syncing scraped data into a SQL database. Using makemigrations and migrate commands ensures the data adheres to a predefined schema. If programmatic access is required, many professional web scraping services provide APIs that deliver JSON data, which can be directly integrated into business intelligence tools. For example, one project successfully processed data for over 40,000 properties across Indian cities into a structured dataset using these methods.
| Export Format | Recommended Tool(s) | Primary Business Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| CSV | Pandas, BeautifulSoup | Data analysis in Excel or Google Sheets |
| JSON / JSONL | Apify API, Python json module |
Integration with web apps and NoSQL databases |
| SQL Database | Django ORM, SQLAlchemy | Long-term storage and complex queries |
| Excel (.xlsx) | Apify, Pandas (openpyxl) | Business reporting and presentations |
Summary and Next Steps
This guide walked you through the essentials of setting up a Python environment and using tools like BeautifulSoup and Selenium to handle both static and dynamic content. Along the way, we tackled common challenges like pagination, cleaning price strings, and standardizing area measurements. These techniques address issues such as dynamic content loading, IP blocking, and data normalization - key steps for scaling your project effectively.
Now it’s time to put this into action. Start small: test your scraper on a single city with a limited number of properties. This will help you validate your logic before expanding. If you're writing a custom script, consider integrating proxies and rate-limiting right from the start to avoid IP bans - some developers have faced authorization issues with basic HTTP requests. For ongoing projects, set up automation with cronjobs to keep your data updated regularly.
Once you've exported clean data in formats like CSV or JSON, dive into analysis. Use tools like Pandas and Matplotlib to uncover trends, spot market opportunities, and evaluate builder performance. For reference, some projects have successfully processed over 40,000 property details across multiple cities using these methods.
The strategies outlined here give you a strong starting point for extracting, cleaning, and analyzing 99acres data at scale.
FAQs
Find answers to commonly asked questions about our Data as a Service solutions, ensuring clarity and understanding of our offerings.
We offer versatile delivery options including FTP, SFTP, AWS S3, Google Cloud Storage, email, Dropbox, and Google Drive. We accommodate data formats such as CSV, JSON, JSONLines, and XML, and are open to custom delivery or format discussions to align with your project needs.
We are equipped to extract a diverse range of data from any website, while strictly adhering to legal and ethical guidelines, including compliance with Terms and Conditions, privacy, and copyright laws. Our expert teams assess legal implications and ensure best practices in web scraping for each project.
Upon receiving your project request, our solution architects promptly engage in a discovery call to comprehend your specific needs, discussing the scope, scale, data transformation, and integrations required. A tailored solution is proposed post a thorough understanding, ensuring optimal results.
Yes, You can use AI to scrape websites. Webscraping HQ’s AI website technology can handle large amounts of data extraction and collection needs. Our AI scraping API allows user to scrape up to 50000 pages one by one.
We offer inclusive support addressing coverage issues, missed deliveries, and minor site modifications, with additional support available for significant changes necessitating comprehensive spider restructuring.
Absolutely, we offer service testing with sample data from previously scraped sources. For new sources, sample data is shared post-purchase, after the commencement of development.
We provide end-to-end solutions for web content extraction, delivering structured and accurate data efficiently. For those preferring a hands-on approach, we offer user-friendly tools for self-service data extraction.
Yes, Web scraping is detectable. One of the best ways to identify web scrapers is by examining their IP address and tracking how it's behaving.
Data extraction is crucial for leveraging the wealth of information on the web, enabling businesses to gain insights, monitor market trends, assess brand health, and maintain a competitive edge. It is invaluable in diverse applications including research, news monitoring, and contract tracking.
In retail and e-commerce, data extraction is instrumental for competitor price monitoring, allowing for automated, accurate, and efficient tracking of product prices across various platforms, aiding in strategic planning and decision-making.