- Harsh Maur
- December 31, 2025
- 9 Mins read
- WebScraping
How to scrape Wayfair Data?
Scraping Wayfair data can help you gather product details like names, prices, ratings, and availability. Here's a quick summary of how to do it:
- Tools Needed: Use Python with libraries like Scrapy, Playwright, Beautiful Soup, and Pandas for scraping and organizing data.
- Challenges: Wayfair uses JavaScript for dynamic content and anti-scraping measures like reCAPTCHA. Tools like Playwright and rotating proxies can help bypass these issues.
-
Steps:
-
Install required Python libraries (
requests,bs4,pandas,scrapy,playwright). - Use Scrapy for crawling and Playwright for handling JavaScript-rendered content.
- Extract product data by targeting specific CSS selectors (e.g., for names, prices, ratings).
- Implement anti-detection techniques like rotating IPs and user agents.
- Save data in CSV, JSON, or databases like MySQL or MongoDB for analysis.
-
Install required Python libraries (
- Legal Considerations: Scraping public data is generally allowed, but avoid violating Wayfair’s terms of service or accessing restricted areas.
This guide walks you through the process step-by-step, ensuring you can collect data efficiently while respecting ethical and legal boundaries.
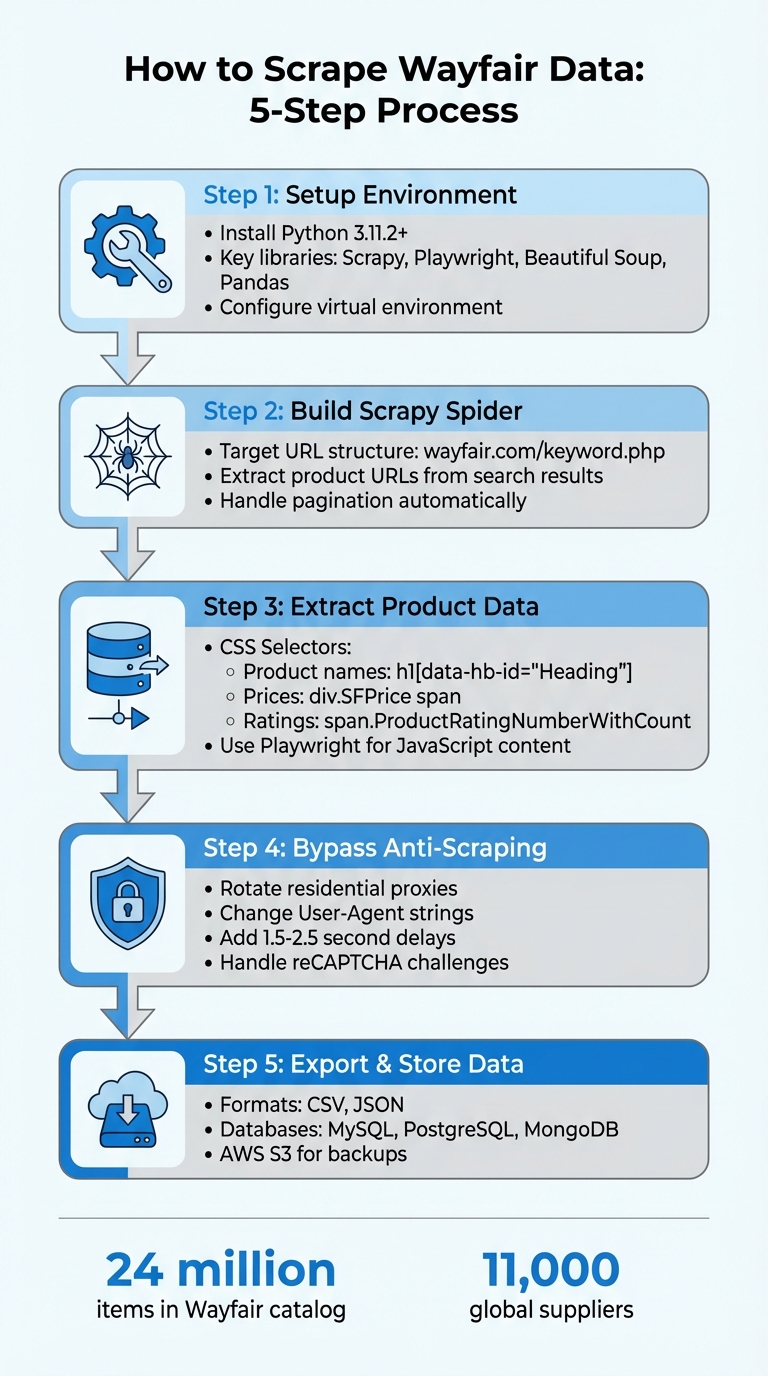
5-Step Process to Scrape Wayfair Product Data
Setting Up Your Scraping Environment
Installing Python and Required Libraries
To get started, make sure you're using Python 3.11.2 or later for seamless compatibility with Wayfair scraping tools.
Install the core libraries by running:
python -m pip install requests bs4 pandas
These libraries are essential for your scraping tasks: Requests handles HTTP requests, BeautifulSoup parses HTML, and Pandas organizes your scraped data into CSV or JSON formats.
For more advanced or large-scale scraping, you'll want to include Scrapy in your toolkit. Install it with:
pip install scrapy scrapeops-scrapy-proxy-sdk
Scrapy simplifies tasks like pagination and complex crawling. If you need to scrape content rendered with JavaScript, add Playwright to your setup:
pip install playwright
playwright install
The playwright install command downloads browser binaries for Chromium, Firefox, and WebKit, enabling you to interact with JavaScript-heavy pages effectively.
Once the libraries are installed, the next step is to configure your environment to manage dependencies efficiently.
Configuring Your Environment
To keep your dependencies organized and avoid conflicts, set up a virtual environment using tools like venv or conda.
For Scrapy, you can configure your data output in settings.py by adding:
FEEDS = {'data/%(name)s_%(time)s.csv': {'format': 'csv'}}
This configuration saves your scraped data directly into a CSV file, with the filename dynamically generated based on the scrape name and timestamp.
When using Playwright, you'll need to account for Wayfair's dynamic content loading. For example, product prices and details are often rendered after the page loads. Use a "wait-for-element" approach to ensure the required data is available. Specifically, wait for CSS selectors like div.SFPrice span to appear before extracting data. Skipping this step could result in capturing empty fields instead of the actual product information.
Finally, to avoid detection by Wayfair's anti-bot systems, set up rotating residential proxies and customize user-agent headers. We'll dive deeper into these anti-detection techniques later.
With your environment ready, you're all set to start scraping data from Wayfair.
Scraping Product Data from Wayfair
Wayfair boasts a massive catalog of over 24 million items sourced from around 11,000 global suppliers. This makes it a treasure trove for anyone conducting competitive analysis or market research. However, pulling data from Wayfair isn’t straightforward - it involves tackling JavaScript-heavy pages that display key details like prices and ratings.
The process can be broken into two main steps: first, a discovery crawler to gather product URLs, and second, a scraper to extract product details. Together, these steps help manage challenges like pagination and dynamic content.
Building a Scrapy Spider for Wayfair
Scrapy is a great choice for crawling multiple pages efficiently. Start by focusing on Wayfair's search URL structure:
https://www.wayfair.com/keyword.php?keyword={keyword}&curpage={page_number}.
Make sure to URL-encode keywords if they include spaces.
Your spider should begin by identifying the total number of pages from the pagination element on the first search results page. Then, increment the curpage parameter to generate requests for the remaining pages. Use Scrapy’s callback system to handle this: the main parse method should collect product URLs and send requests to a parse_product_data method, which will extract specific product details.
For extracting data, target these CSS selectors:
-
Product names:
h1[data-hb-id="Heading"] -
Prices:
div.SFPrice span.oakhm64z_6112 -
Ratings:
span.ProductRatingNumberWithCount-rating
You can configure Scrapy’s settings.py file to export this data automatically using the FEEDS setting. While Scrapy does a solid job with pagination, handling JavaScript-rendered content requires additional tools.
Using Playwright for JavaScript-Rendered Content
To deal with Wayfair’s dynamic content, a headless browser like Playwright is essential. It ensures all elements that load after the initial HTML are fully rendered before scraping.
Playwright’s wait_for_selector method is key here. Use it to wait for critical elements - like div.SFPrice span - to appear, ensuring complete data capture. Skipping this step could result in missing or empty fields. To improve performance, you can optimize by intercepting non-essential resources.
Finally, to avoid anti-scraping measures, integrate natural delays and rotate proxies as part of your scraping strategy. These steps will help ensure smooth and uninterrupted data collection.
Overcoming Anti-Scraping Measures
Wayfair employs Google's reCAPTCHA, browser fingerprinting, and behavioral pattern recognition to identify and block automated scraping attempts. A common red flag is sending multiple requests from the same IP address in quick succession, which can activate these defenses. When this happens, you might encounter a reCAPTCHA challenge or receive a 429 (Too Many Requests) error.
Rotating User Agents and Using Proxies
To avoid detection, opt for residential proxies rather than datacenter IPs. Residential proxies are tied to real household devices, making them appear more like legitimate users to Wayfair's systems. Many premium providers offer extensive networks of residential proxies tailored for scraping needs.
In addition to rotating IP addresses, change your User-Agent strings and HTTP headers with each request to simulate activity across various browsers. Adjust headers such as Accept-Language, DNT, and Connection to emulate traffic from browsers like Chrome, Firefox, and Safari on both desktop and mobile platforms.
Residential proxies typically cost about $80 for unmetered access or $15 for premium geo-targeted options. Meanwhile, datacenter proxies are priced between $50 and $120. Many providers also offer free trials, often ranging from 50MB to 1GB, allowing you to test their networks before committing.
Once proxies and headers are in place, the next step is to manage request timing and handle CAPTCHAs effectively.
Handling Rate Limiting and CAPTCHAs
Rate limiting presents a significant challenge when scaling scraping operations on Wayfair. To bypass this, introduce random delays between requests - using tools like time.sleep() - with intervals ranging from 1.5 to 2.5 seconds. This helps mimic human browsing behavior and avoids triggering defenses.
When faced with CAPTCHAs, consider using stealth browser libraries like Playwright Stealth or integrating CAPTCHA-solving services. Save solution cookies, such as cf_clearance, to minimize repeated challenges.
Be cautious with hidden elements, often referred to as honeypots. Wayfair may include invisible links or form fields designed to catch bots. Focus only on visible, user-accessible elements, and always test your selectors manually in a browser to ensure accuracy and avoid immediate bans.
sbb-itb-65bdb53
Legal and Ethical Considerations for Scraping Wayfair
Before diving into scraping Wayfair's public data, it's crucial to understand the legal framework. The Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA) does not apply to public websites, as clarified by the Ninth Circuit's decision in HiQ v. LinkedIn. Ondra Urban, COO of Apify, explains:
"The US courts have consistently upheld the legality of web scraping of publicly available data from the internet if conducted appropriately".
This means scraping details like product names, prices, and availability from Wayfair’s public pages is permissible, provided you don’t bypass login walls or authentication measures.
Copyright law comes into play when dealing with creative content, such as product descriptions or original images, which are protected. However, factual data like prices and stock levels are not covered by copyright. To stay on the right side of the law, transform the data you collect - such as using HTML product listings to build a price comparison tool - instead of replicating Wayfair’s content to compete directly . If your scraping involves user reviews or profiles, remember that the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) regulates personal data. That said, publicly available information generally faces fewer restrictions.
Respecting Terms of Use and robots.txt
Legal considerations aside, you should also adhere to Wayfair's website guidelines to maintain compliance. Start by reviewing the robots.txt file at wayfair.com/robots.txt. This file specifies which parts of the site the owner prefers not to have crawled using the Disallow command. While ignoring robots.txt isn’t illegal in the U.S., it crosses an ethical line and could be cited against you in legal disputes.
Pay close attention to Wayfair's Terms of Service (ToS). "Clickwrap" agreements - where you actively agree to terms by clicking "I Agree" or logging in - are legally binding and enforceable. If accessing certain data requires accepting such terms, scraping that content could expose you to legal risks. To avoid issues, focus on publicly accessible pages that don’t require authentication or agreement clicks.
Best Practices for Ethical Scraping
Ethical scraping goes beyond legal compliance and requires thoughtful execution. Limit the frequency of your requests to avoid overloading Wayfair’s servers or triggering denial-of-service (DoS) protections. Introduce random delays between requests and consider scraping during off-peak hours to mimic natural browsing behavior.
Use the data you collect responsibly. For instance, analyze Wayfair’s product information for market trends, price tracking, or competitive research. Avoid republishing their content to create a replica store. Stick to public data like product specifications, ratings, and pricing. By following these practices, you can ensure your scraping efforts remain both lawful and respectful of Wayfair's resources and user privacy.
Exporting and Storing Wayfair Data
Saving Data in CSV or JSON Formats
Once you've gathered product details, the next step is to organize and save the data for analysis. A common practice is to export the scraped data into CSV or JSON formats. To do this effectively, you can load your data - usually a list of dictionaries - into a Pandas DataFrame. This allows you to clean and structure fields like product titles, prices, ratings, and URLs before exporting.
For a CSV file, use to_csv(index=False) to ensure the data is saved without unnecessary indexing. If you prefer JSON, use orient='records' along with UTF-8 encoding to handle special characters often found in product descriptions. This ensures your data remains intact and readable.
If you're working with Scrapy, you can streamline this process by setting up Feed Exports in your settings.py file. By using dynamic file paths with variables like %(name)s and %(time)s, you can automatically generate unique file names. This is especially handy for keeping a historical record of your scrapes.
Storing Data in Databases
For projects that require frequent updates or more advanced data queries, storing your data in a database is a smart move. Relational databases such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, or SQLite work well for structured product data. Alternatively, if you're dealing with nested details like product variants or feature lists, MongoDB is a great option. Databases are particularly useful for managing large inventories and ensuring scalability.
To automate this process, use Scrapy pipelines to insert items directly into your database. Before storing the data, clean up price strings by removing currency symbols and converting them into numerical values. Similarly, extract ratings as numbers to simplify SQL-based analysis. For high-volume operations, consider using AWS S3 buckets to store files either before or alongside database ingestion. This adds an extra layer of durability and provides a reliable backup solution.
Conclusion
Scraping Wayfair's catalog of over 24 million items opens the door to valuable insights like pricing trends, inventory changes, and customer sentiment - key elements for shaping your strategy. This guide walked you through setting up Python with tools like Scrapy and Playwright, extracting product details from both static and JavaScript-rendered pages, and tackling anti-scraping challenges with techniques like rotating proxies and user-agent management. These technical skills form the backbone of web scraping for beginners and advanced users alike.
However, the technical side is just one piece of the puzzle. Adhering to ethical practices - such as respecting robots.txt files and spacing out your requests - ensures that your scraping efforts are both responsible and sustainable. This approach helps you avoid IP bans and stay within Wayfair's terms of service.
Once your data is collected, you can export it in formats like CSV or JSON, or store it in a database to enable real-time analysis and trend forecasting. These steps ensure your scraping efforts translate into actionable insights.
FAQs
Find answers to commonly asked questions about our Data as a Service solutions, ensuring clarity and understanding of our offerings.
We offer versatile delivery options including FTP, SFTP, AWS S3, Google Cloud Storage, email, Dropbox, and Google Drive. We accommodate data formats such as CSV, JSON, JSONLines, and XML, and are open to custom delivery or format discussions to align with your project needs.
We are equipped to extract a diverse range of data from any website, while strictly adhering to legal and ethical guidelines, including compliance with Terms and Conditions, privacy, and copyright laws. Our expert teams assess legal implications and ensure best practices in web scraping for each project.
Upon receiving your project request, our solution architects promptly engage in a discovery call to comprehend your specific needs, discussing the scope, scale, data transformation, and integrations required. A tailored solution is proposed post a thorough understanding, ensuring optimal results.
Yes, You can use AI to scrape websites. Webscraping HQ’s AI website technology can handle large amounts of data extraction and collection needs. Our AI scraping API allows user to scrape up to 50000 pages one by one.
We offer inclusive support addressing coverage issues, missed deliveries, and minor site modifications, with additional support available for significant changes necessitating comprehensive spider restructuring.
Absolutely, we offer service testing with sample data from previously scraped sources. For new sources, sample data is shared post-purchase, after the commencement of development.
We provide end-to-end solutions for web content extraction, delivering structured and accurate data efficiently. For those preferring a hands-on approach, we offer user-friendly tools for self-service data extraction.
Yes, Web scraping is detectable. One of the best ways to identify web scrapers is by examining their IP address and tracking how it's behaving.
Data extraction is crucial for leveraging the wealth of information on the web, enabling businesses to gain insights, monitor market trends, assess brand health, and maintain a competitive edge. It is invaluable in diverse applications including research, news monitoring, and contract tracking.
In retail and e-commerce, data extraction is instrumental for competitor price monitoring, allowing for automated, accurate, and efficient tracking of product prices across various platforms, aiding in strategic planning and decision-making.